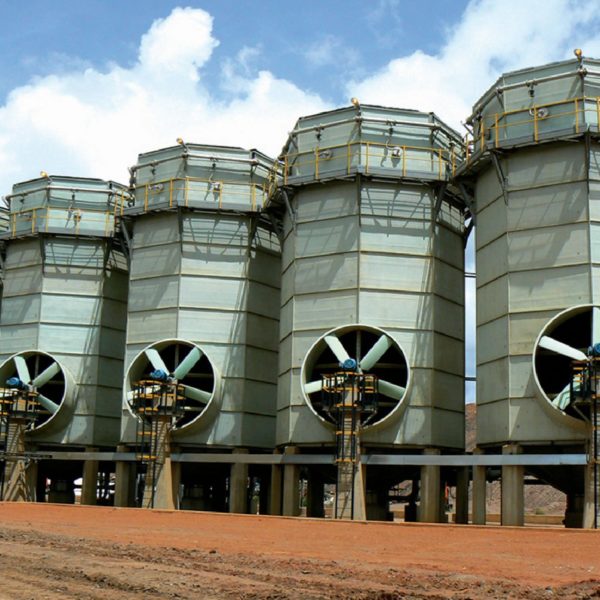
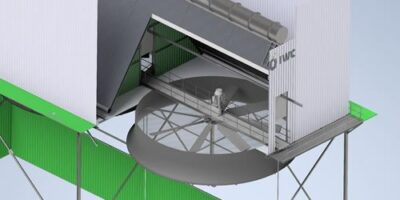
Field Erected Cooling Towers
Our field erected cooling towers are constructed from various materials such as GRP and concrete to steel and timber. Our design engineers select from a number of possible cooling tower component combinations that result in economical selections, capable of the performance required.




A cooling tower is a heat exchanger, inside of which heat is withdrawn from the water by contact between the water and the air. Cooling towers use water evaporation to reject heat from processes such as cooling the circulating water used in oil refineries, chemical plants, power plants, steel mills and food processing plants.
An industrial water cooling tower extracts waste heat to the atmosphere though the cooling of a water stream to a lower temperature. Towers that use this process are called evaporative cooling towers.
The process is called “evaporative” because it allows a small portion of the water being cooled to evaporate into a moving air stream, providing significant cooling to the rest of that water stream. The heat from the water stream transferred to the air stream raises the air’s temperature and its relative humidity to 100%, and this air is discharged to the atmosphere.
Evaporative heat rejection devices – such as industrial cooling systems – are commonly used to provide significantly lower water temperatures than achievable with “air-cooled” or “dry” heat rejection devices, like the radiator in a car, thereby achieving more cost-effective and energy efficient operation of systems in need of cooling.
Industrial water cooling towers vary in size from small roof-top units to very large hyperboloid (hyperbolic) structures that can be up to 200 metres tall and 100 metres in diameter, or rectangular structures that can be over 15 meters tall and 40 meters long. Smaller towers (package or modular) are normally factory-built, while larger ones are typically constructed on site in various materials.
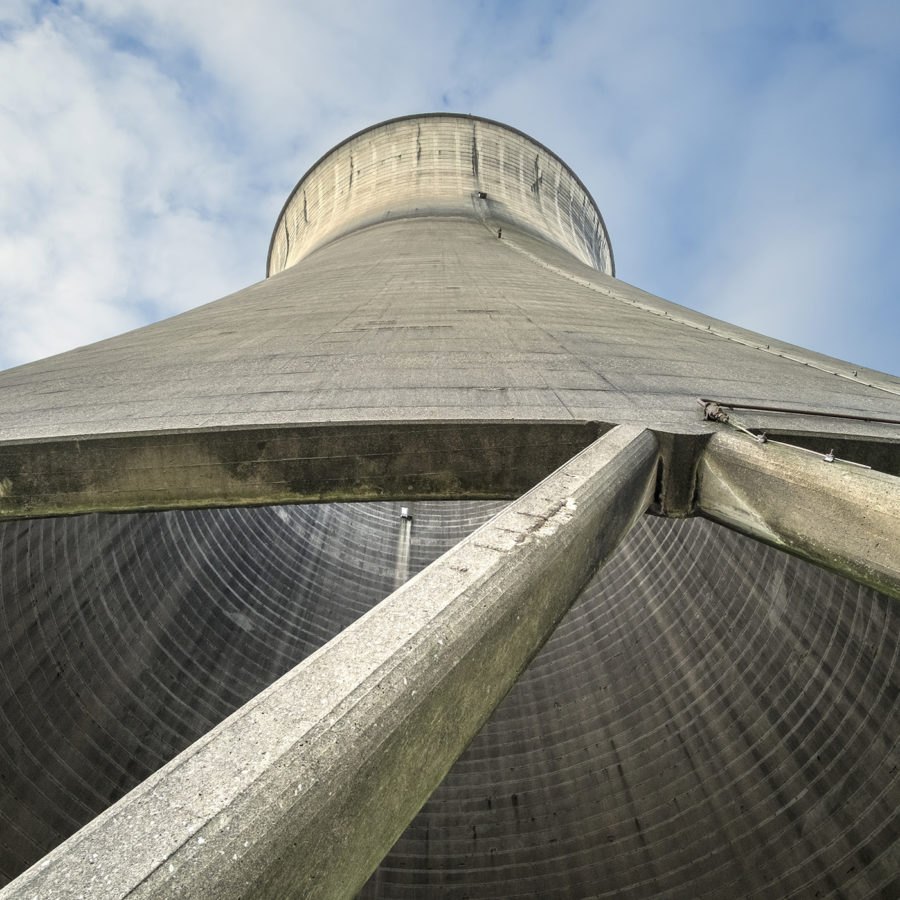

Concrete Field Erected
Concrete is a natural material which is ideally suited for long service life in the harshest environment and defies the detrimental effects of heat and ultraviolet light.
IWC has an impressive installed base of cast in situ concrete cooling towers, across a number of different industries, and countries. Cast in situ concrete cooling tower structures have a superior lifespan and generally require very little, to no maintenance when compared to other materials of construction.
Advantages
- Good chemical and corrosion resistance
- Exceptional service life
Various types of fill can be used, which are dependent on the application and water quality. Some fills on offer are:
- Film Packs – Clean water
- Trickle Packs – Moderately dirty water
- Splash Packs – Dirty water
- Splash Bars – Very dirty water
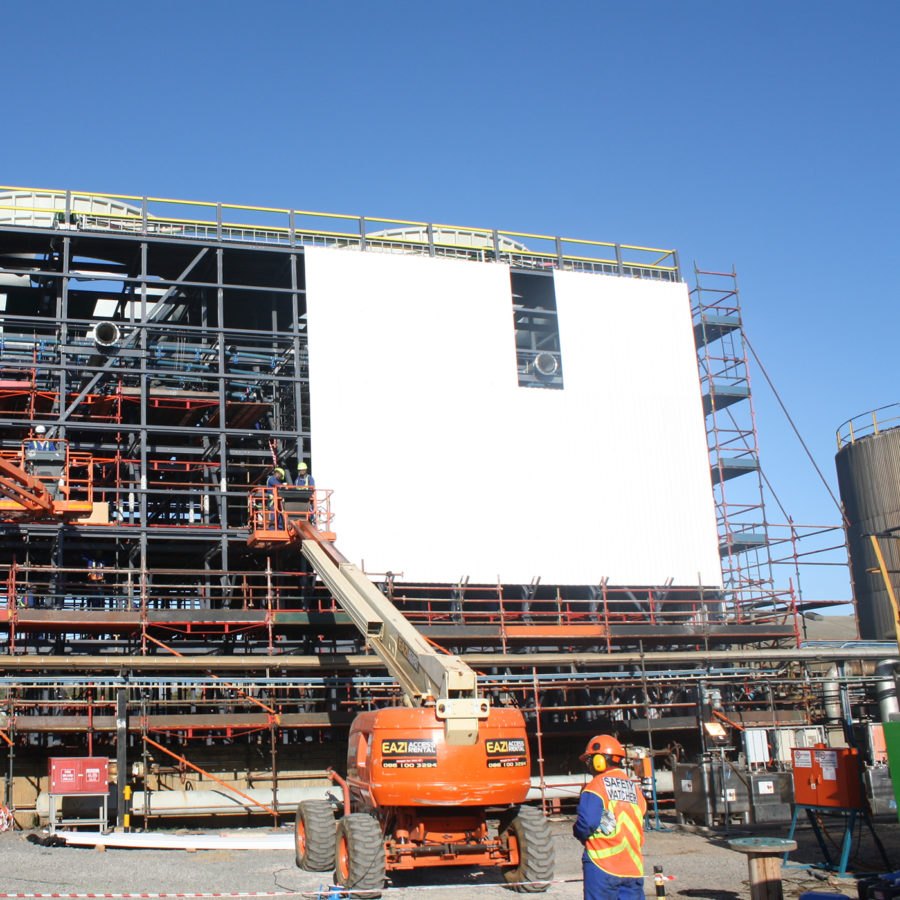



Pultruded GRP Field Erected Cooling Towers
Our pultruded GRP towers are built according to precise project specifications and conform to CTI STD-137 & CTI STD-152 standards.
Due to the unique properties of Glass Reinforced Polyester (GRP), pultruded GRP is becoming the industry norm for the construction of large field erected cooling towers, and owners and operators can benefit from long service life of cooling towers constructed from pultruded GRP. Construction durations are reduced as well as the initial capital cost. These cooling towers can be rapidly deployed to remote project sites and assembled with limited skills, plant, and equipment.
Advantages
- Exceptional chemical and corrosion resistance
- Resistance to all types of “aggressive” water (for example sea water)
- Resistance to weather conditions
- High impact strength
- Rigidity
- Light weight
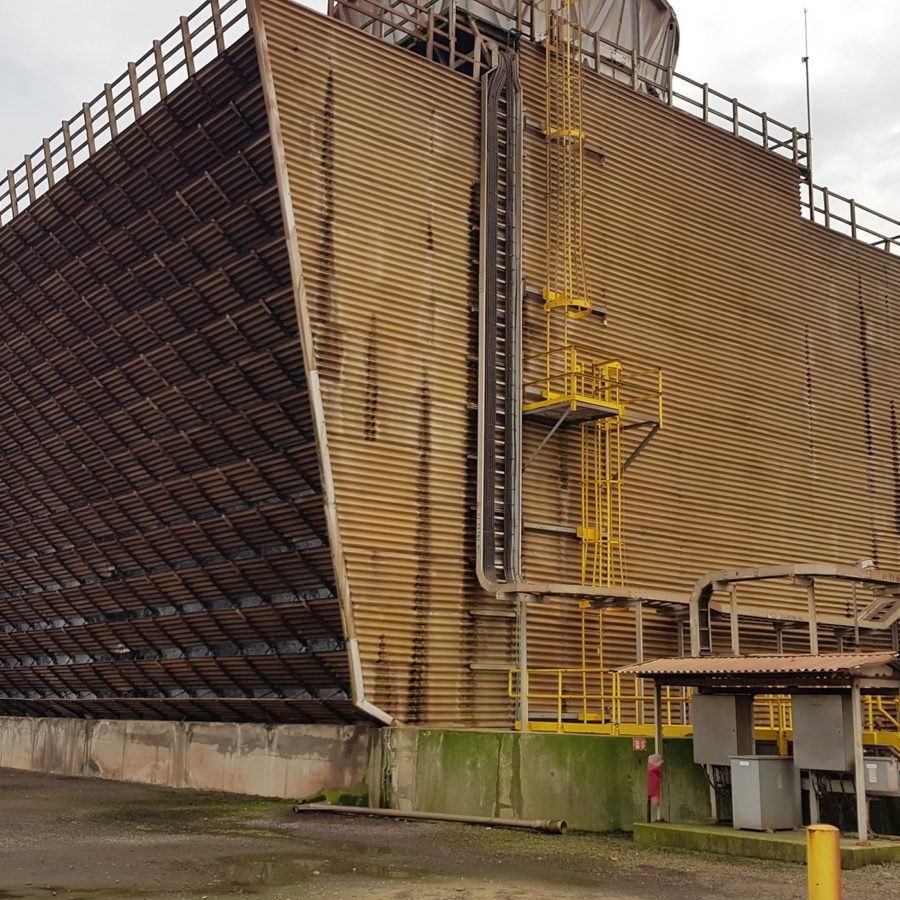

Steel & Timber
IWC can construct cooling towers from other materials to suit customers’ requirements, the choice of material for the cooling tower structure is largely dependent on the cooling water chemistry.
Some of the materials that are widely used for cooling tower structures are:
- Clad carbon steel – hot dip galvanized or coated
- Clad stainless-steel structures (various grades)
- Clad treated timber structures

More Cooling Towers Solutions